Review: [Specific Chain Restaurant] Healthy Options?
Evaluating Protein Sources: A Comprehensive Look
Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues, maintaining a healthy immune system, and supporting various bodily functions. Choosing the right protein sources is crucial for a balanced diet and overall well-being. Understanding the different types of protein and their nutritional value is key to making informed dietary choices. We need to consider not only the amount of protein but also the quality and digestibility of the source.
Various protein sources offer different nutritional profiles. Grasping the nuances of these differences is paramount to tailoring your protein intake to your specific needs. For example, animal-based proteins often provide complete proteins, containing all essential amino acids. Plant-based proteins, while valuable, may require combining different sources to obtain all essential amino acids.
Animal Protein Sources: Meat, Poultry, and Fish
Animal protein sources like meat, poultry, and fish are excellent sources of high-quality protein. They are often complete proteins, meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids the body needs. Red meat, in particular, provides iron, a crucial mineral for various bodily functions. However, excessive consumption of red meat can be linked to certain health concerns, so moderation is key.
Poultry is a leaner protein option compared to red meat, offering a good balance of protein and nutrients. Fish, particularly fatty fish like salmon, provides omega-3 fatty acids, beneficial for heart health and brain function. The specific nutritional value of each animal protein source varies depending on the cut, preparation method, and the animal itself.
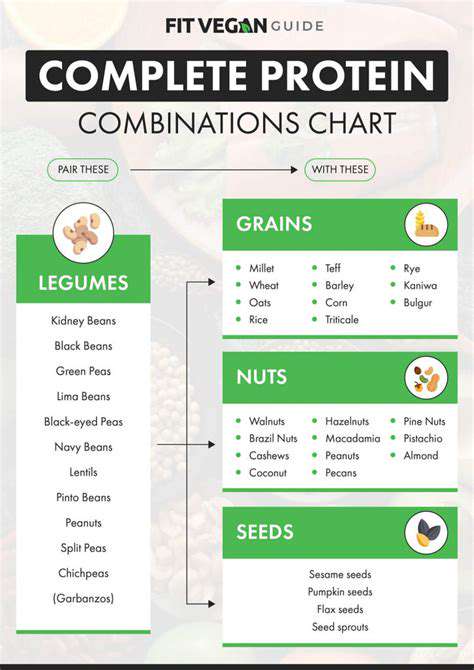
Plant-Based Protein Sources: Legumes, Nuts, and Seeds
Plant-based protein sources like legumes, nuts, and seeds are valuable additions to a balanced diet. Legumes, including beans and lentils, are excellent sources of protein and fiber, promoting healthy digestion. They are often a more affordable and sustainable option compared to animal-based proteins.
Nuts and seeds provide a concentrated source of protein, healthy fats, and essential vitamins and minerals. They can be incorporated into various meals and snacks, adding texture and flavor. However, they are often higher in calories, so portion control is important.
Dairy Protein Sources: Milk, Yogurt, and Cheese
Dairy products, such as milk, yogurt, and cheese, are excellent sources of protein and calcium, crucial for bone health. They are often complete proteins, providing all essential amino acids. Dairy products can be incorporated into various meals, from breakfast cereals to desserts. Their nutritional value depends on the type of dairy product and the processing methods used.
Choosing low-fat or fat-free options can help manage calorie intake while still reaping the benefits of protein and calcium. However, some individuals may experience digestive issues with dairy products due to lactose intolerance.
Protein Intake and Individual Needs: Considerations
Protein requirements vary depending on factors like age, activity level, and overall health. Athletes often need higher protein intakes to support muscle growth and recovery. Pregnancy and breastfeeding also increase protein needs. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian can help determine the appropriate protein intake for individual needs. Understanding your personal requirements is critical to achieving optimal health and well-being.
Protein quality and digestibility also play a role. Different protein sources have varying biological values, reflecting how effectively the body can use the protein for its intended purpose. Choosing diverse protein sources can optimize the intake of essential amino acids and ensure adequate protein synthesis.
Protein Sources and Health Concerns: Allergies and Sensitivities
It's important to be mindful of potential allergies or sensitivities to certain protein sources. Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to peanuts, tree nuts, soy, or other specific proteins. Careful attention to food labels and ingredient lists is essential to avoid potential allergic reactions.
Certain protein sources may also trigger digestive issues, such as lactose intolerance or gluten sensitivity. Being aware of these sensitivities is crucial to maintaining overall digestive health. Consulting a healthcare professional about potential dietary restrictions or sensitivities is highly recommended.

Read more about Review: [Specific Chain Restaurant] Healthy Options?
Hot Recommendations
- Traditional Foods for Day of the Dead
- Food Etiquette in Italy: Pasta Rules!
- Best Family Friendly Restaurants with Play Areas in [City]
- Review: The Best [Specific Dessert] Place in [City]
- Top Ice Cream Parlors in [City]
- Traditional Foods for Halloween
- The History of the Potato in Ireland
- Best Vegan Pizza Joints in [City] [2025]
- Best Bakeries for Sourdough Bread in [City]
- Food Culture in Argentina: Asado and Wine

![Review: [Specific Wine Bar Name] with Food Pairing](/static/images/28/2025-05/FinalThoughts3AAMust-VisitforWineEnthusiastsandFoodies.jpg)
![Review: [Specific Cuisine] Restaurant Experience in [City]](/static/images/28/2025-05/FinalThoughts3AAHighlyRecommendedDiningDestination.jpg)



![Review: The [Specific Brand] Digital Meat Thermometer](/static/images/28/2025-05/ValueforMoney3AABalancedAssessment.jpg)




